Blind Reversal Is Still Blind Care—Even with Sugammadex
Evidence that sugammadex without quantitative monitoring is not safe.
Read MoreEvidence-based perspectives on recovery, stewardship, and workflow efficiency.
Evidence that sugammadex without quantitative monitoring is not safe.
Read More
Incomplete reversal and recurrent neuromuscular blockade can occur for reasons that we don’t actually understand.
Read More
A Step-by-Step Guide for Anesthesia Departments
Read More
In the final article of this clinical review, the focus shifts from evidence and economics to implementation—specifically, how training, workflow ...
Read More
Building on the patient safety evidence reviewed in part 1, this second article examines the economic implications of residual neuromuscular ...
Read More
This first article in a three-part clinical review examines the patient safety evidence behind quantitative neuromuscular monitoring, with a focus on ...
Read More
A 2025 review of neuromuscular monitoring myths, acceleromyography limitations, and why quantitative EMG monitoring is essential for safer anesthesia ...
Read More
Blink Anesthesia advances quantitative neuromuscular monitoring with TwitchView® innovations, large-scale hospital deployments, and a clinician-first ...
Read More
Blink Anesthesia deploys 119 TwitchView® EMG-based TOF monitors at a top U.S. academic hospital, reinforcing quantitative neuromuscular monitoring as ...
Read More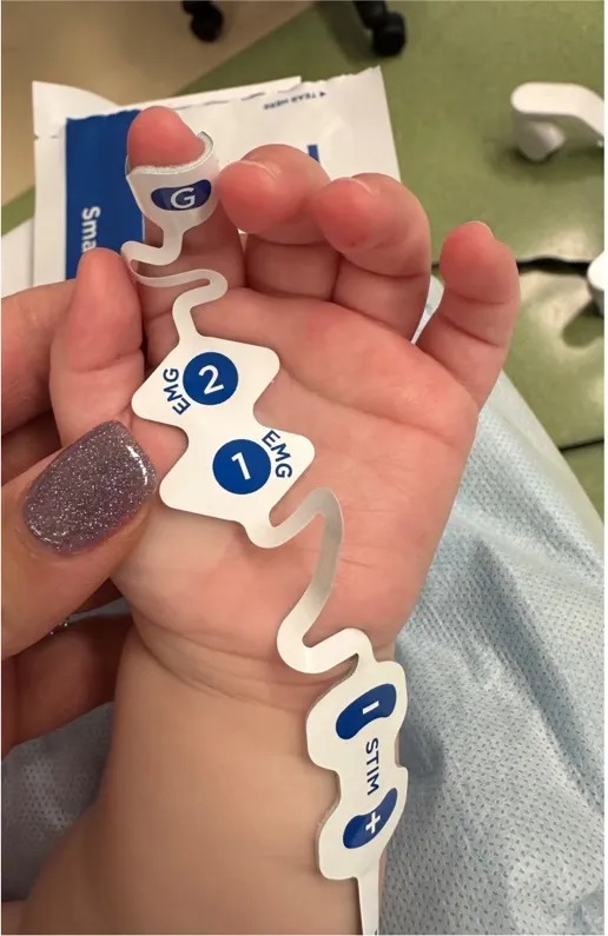
Three ulnar-innervated hand muscles are commonly used for train-of-four monitoring. Emerging evidence shows they don’t all behave the same.
Read More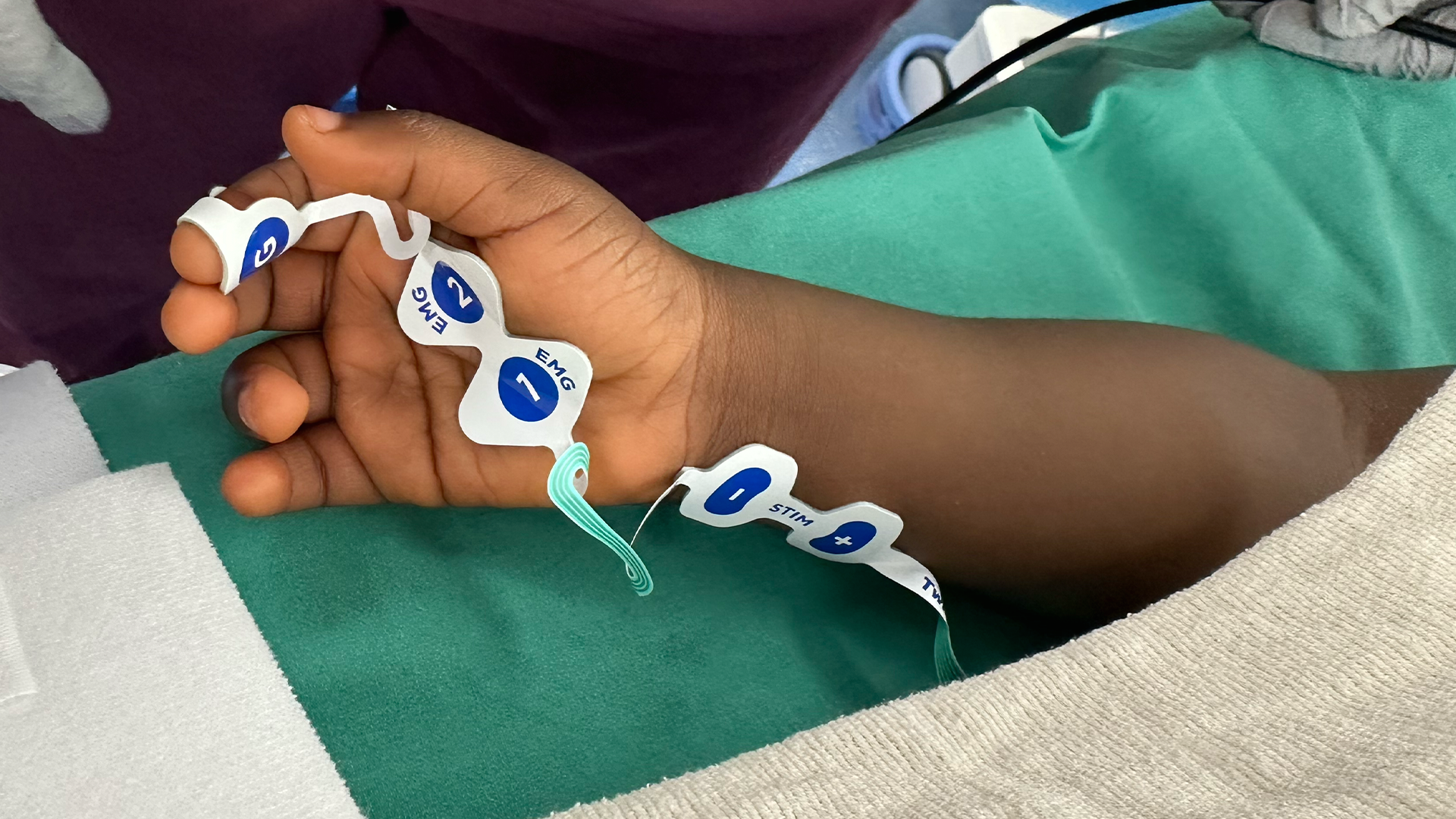
Three ulnar-innervated hand muscles are commonly used for train-of-four monitoring. Emerging evidence shows they don’t all behave the same.
Read More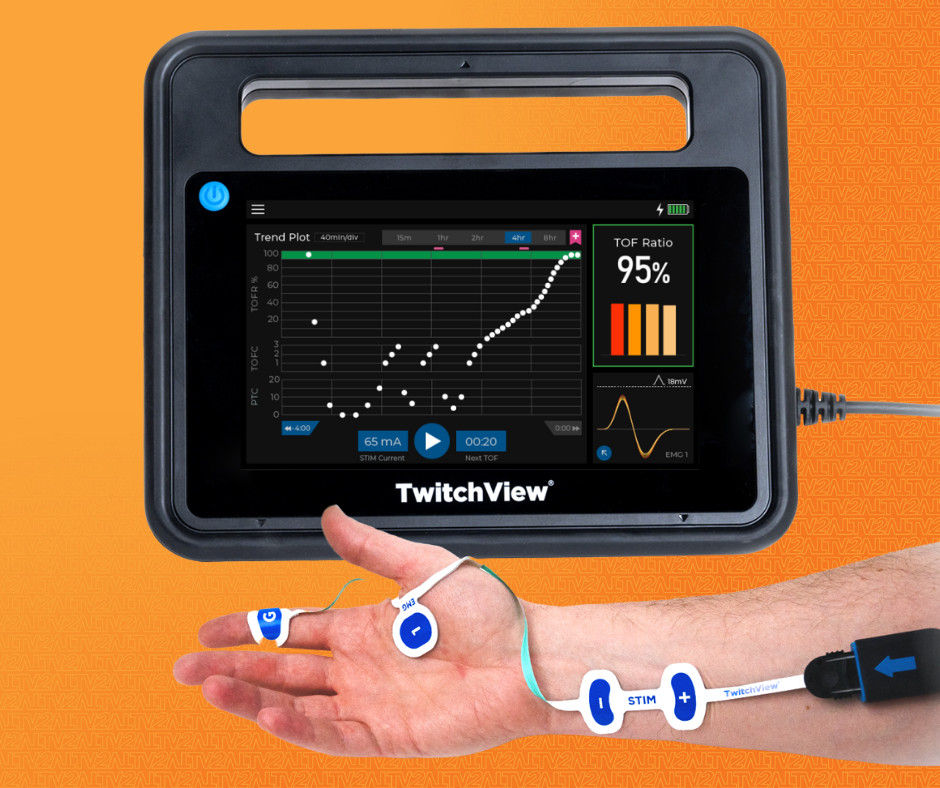
Residual paralysis affects up to 40% of patients without quantitative monitoring. Learn what 0% residual paralysis looks like in clinical practice, ...
Read More
Residual neuromuscular block affects up to 40% of surgical patients without objective monitoring. Learn why EMG-based tools like TwitchView are ...
Read More
Are continuous muscle relaxant infusions superior to bolus dosing? Explore expert insights on optimizing neuromuscular blockade in anesthesia ...
Read More
Explore what the ASA guidelines actually say about neuromuscular monitoring—and whether your practice is aligned with today’s standards of care.
Read More
Learn how quantitative EMG monitoring outperforms subjective twitch assessments in reducing residual paralysis and improving patient outcomes.
Read More
Discover how Blink was built in partnership with anesthesiologists to solve a real problem: unreliable Train of Four (TOF) monitoring.
Read More
Discover how proper electrode placement can enhance the accuracy and trust in quantitative neuromuscular monitoring, based on recent research ...
Read More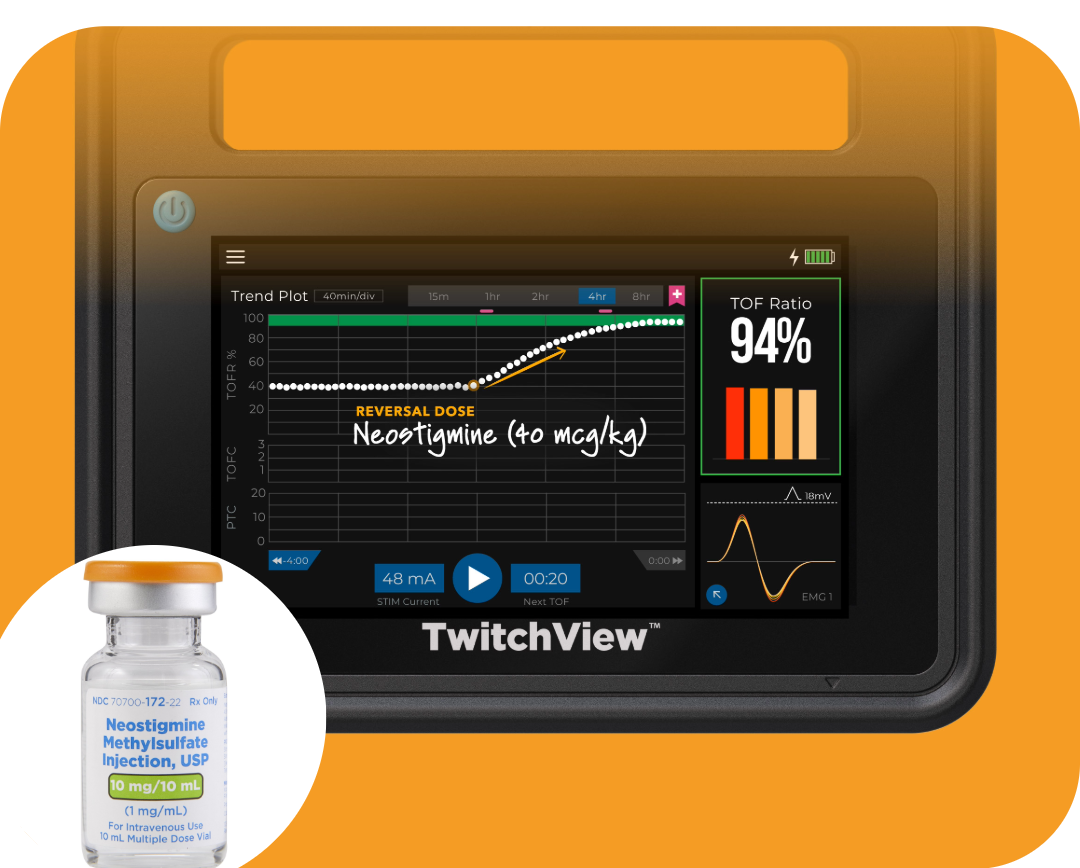
Explore the limitations of neostigmine in reversing neuromuscular blockade and discover its niche applications.
Read More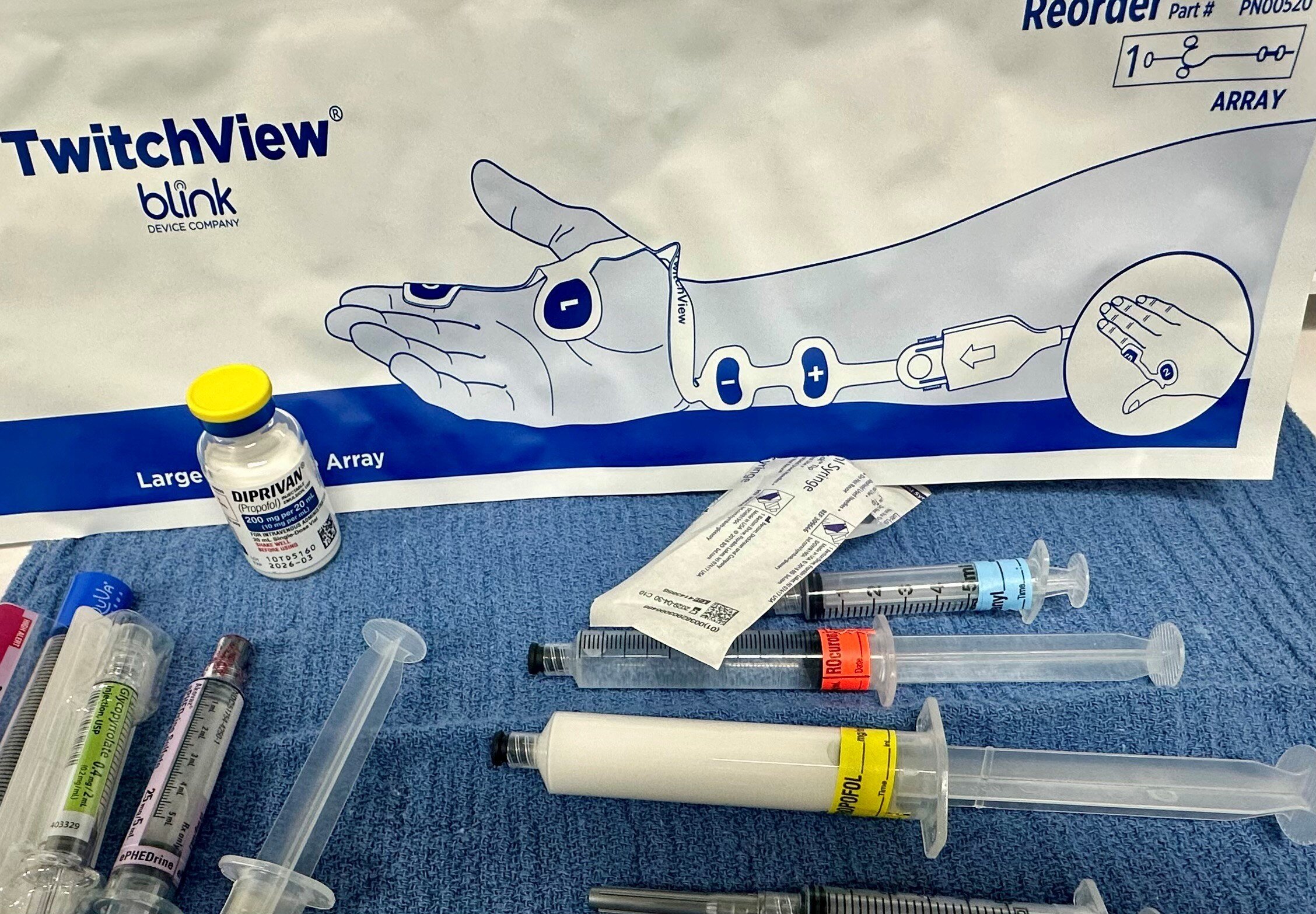
Understand strategies to prevent patient movement during surgery using neuromuscular blockers and opioids.
Read More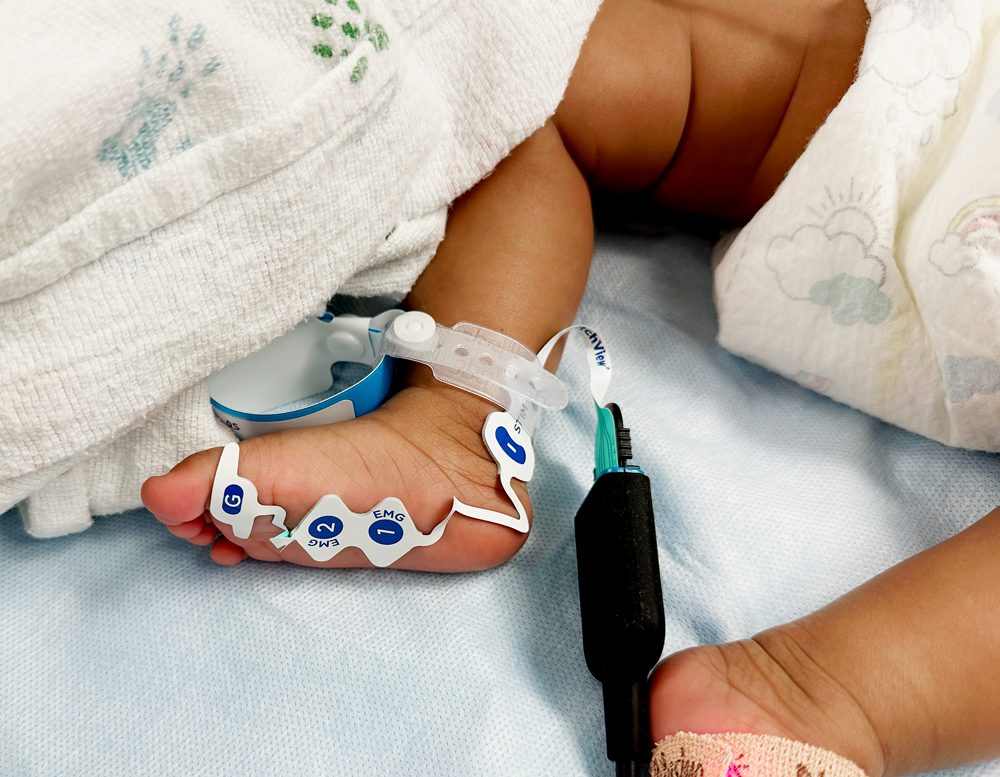
Examine how quantitative neuromuscular monitoring can prevent adverse events in pediatric patients.
Read More
Understand how neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs) affect various muscles, including their onset and duration of action.
Read More
Residual paralysis affects up to 40% of patients without quantitative monitoring. Learn what 0% residual paralysis looks like in clinical practice, ...
Read More
Quantitative TOF monitoring of neuromuscular blockade plays a crucial role in modern anesthesia practice and continues to improve patient care.
Read More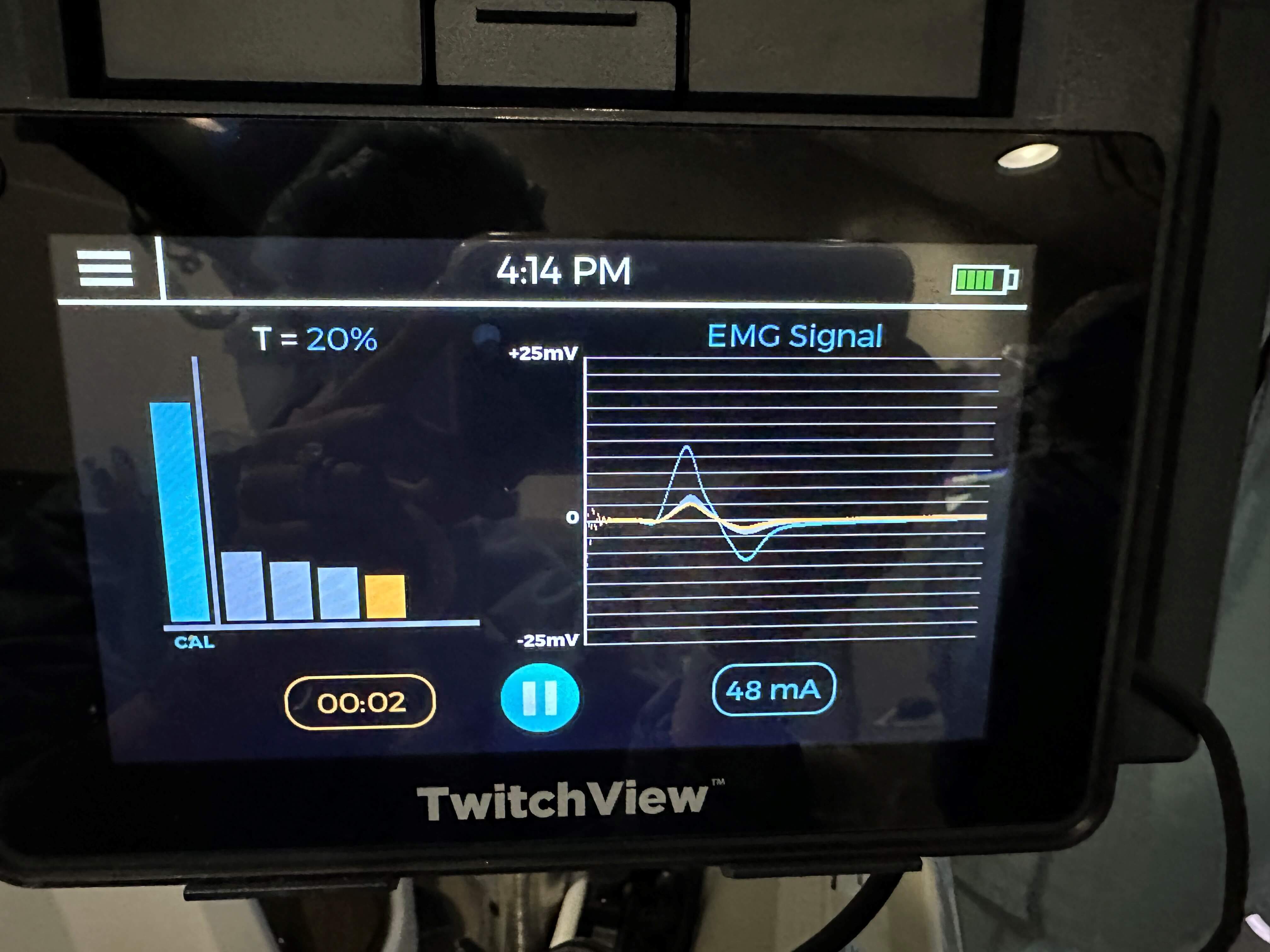
Instructions for monitoring succinylcholine-induced neuromuscular blockade and a review of pseudocholinesterase deficiency.
Read More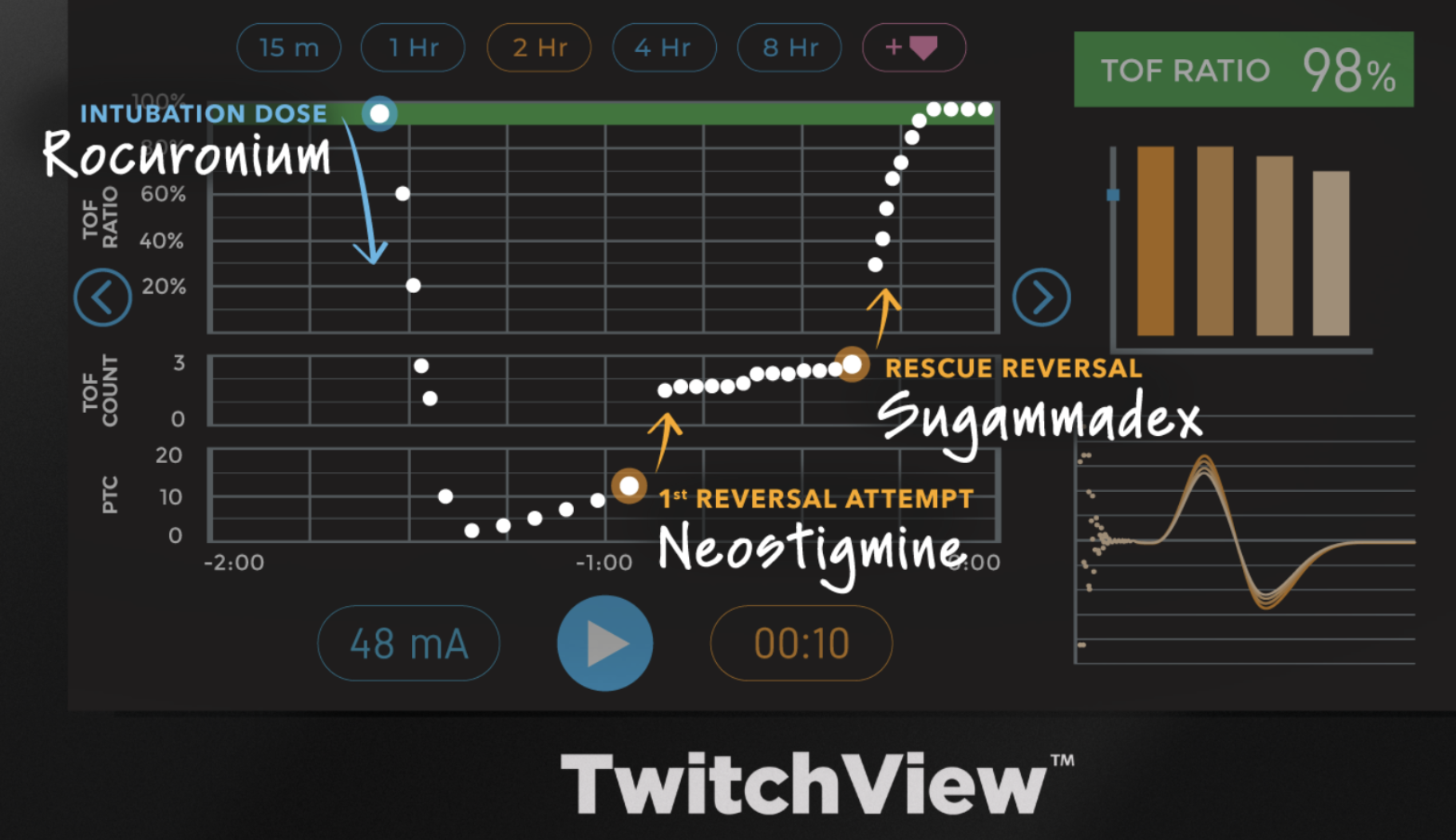
Why the ASA Guidelines recommend train-of-four measurements of the adductor pollicis with quantitative monitoring over a peripheral nerve stimulator ...
Read More
Step-by-step guide to implementing quantitative neuromuscular monitoring as recommended by the ASA practice guidelines.
Read More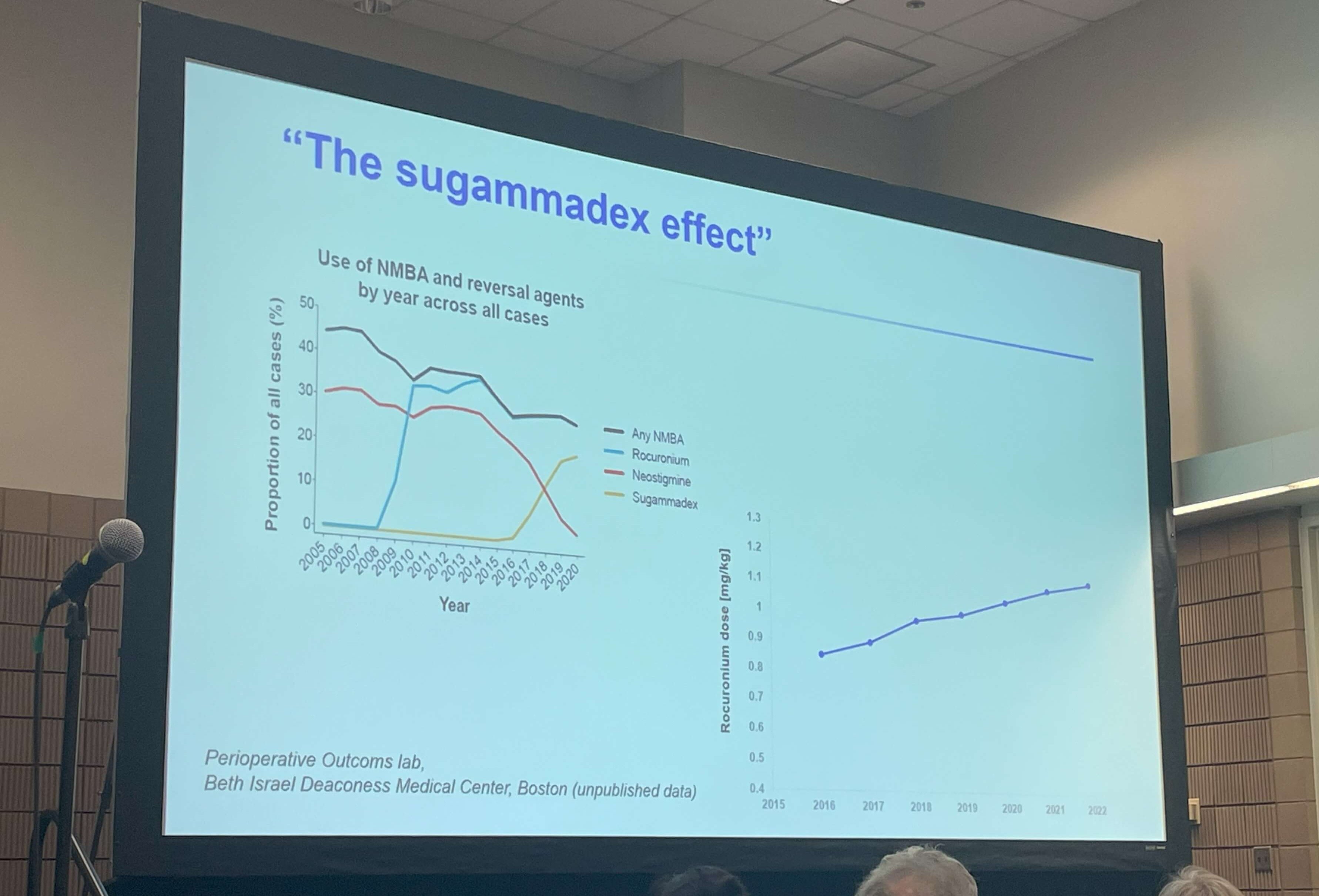
Eliminate post-operative residual neuromuscular blockade (PRNMB) using protocol and guideline recommendations for quantitative train of four.
Read More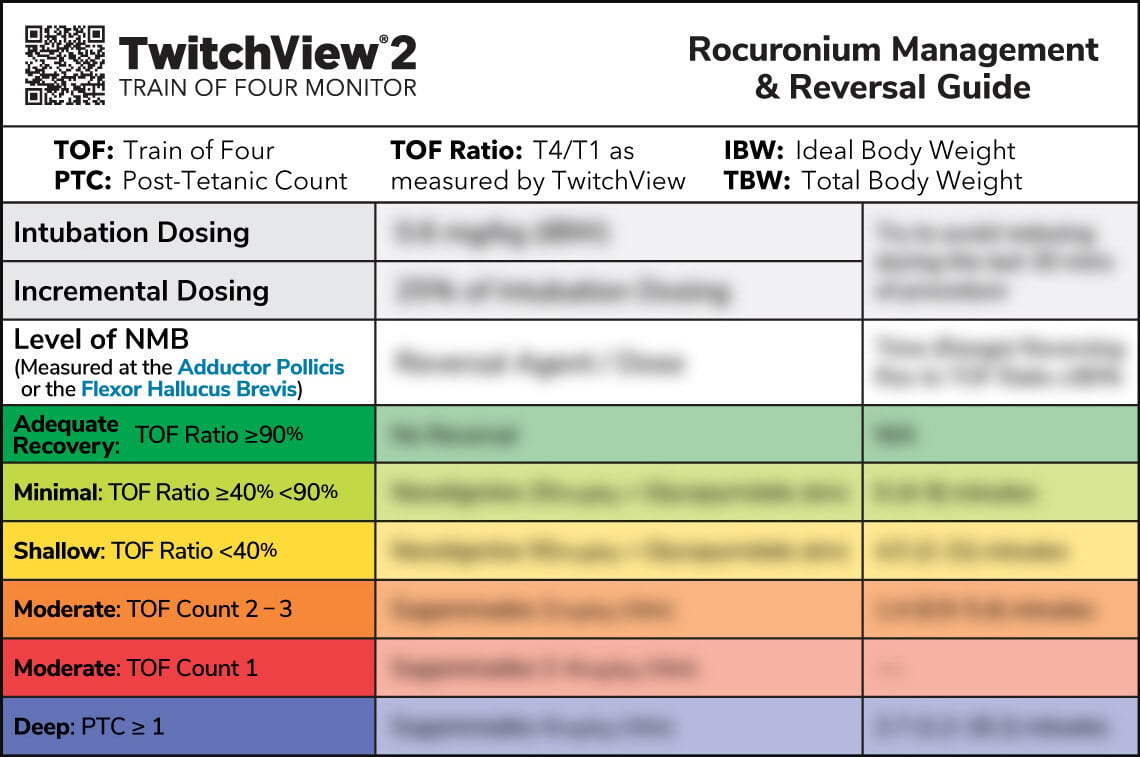
ASA Guidelines for Monitoring Neuromuscular Blockade. First author, Dr. Stephan Thilen discusses Reversal Guides, Reversal Protocols and Antagonism ...
Read More
Gold-standard mechanomyography (MMG) vs electromyography (EMG) vs acceleromyography (AMG). Advances in quantitative neuromuscular monitoring.
Read MoreTry selecting a different topic or check back later for new content.
Even with 100% sugammadex use, the incidence of residual paralysis rates remains as high as 10% without quantitative monitoring2
No. Clinical tests such as head lift or hand grip cannot detect residual block above TOF ratios of 0.4. Only quantitative monitoring confirms TOF ≥0.9, the threshold for safe recovery5
Residual paralysis increases risk of airway obstruction, hypoxemia, and postoperative pulmonary complications. A landmark study using quantitative monitoring with the TwitchView Train Of Four Monitor eliminated residual paralysis5
The TwitchView TOF Monitor is meticulously designed with robust cables, durable screens, rugged design— all backed by a market-leading warranty in the U.S.
Yes. Electrode arrays are available for infants, children, and adults. A key advantage of EMG monitoring is that it works even when patients’ hands are tucked.
Active noise canceling eliminates noise at the source, ensuring even the tiniest twitches are accurately captured.
Yes. TwitchView connects with most anesthesia information systems and EHRs, automatically exporting data to the patient record.
Quantitative monitoring reduces postoperative complications, shortens recovery times, and lowers readmission risk. Preventing even a few pulmonary complications offsets the cost of monitoring3. In addition, many institutions see substantially reduced drug costs. Beyond savings, hospitals gain improved outcomes, increased provider confidence, and compliance with the 2023 American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Guidelines for Monitoring and Antagonism of Neuromuscular Blockade5 and the 2023 European Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care (ESAIC) Guidelines for Perioperative Management of Neuromuscular Blockade12.
Answer a few quick questions, and we’ll prepare a customized report showing how much your hospital could save by reducing residual paralysis and optimizing reversal drug use. See your potential impact in dollars, tailored to your institution.