
Experts have used TwitchView to eliminate residual neuromuscular blockade and facilitate spontaneous recovery in 20% of general anesthetic cases enhancing patient safety and reducing unnecessary hospital expenses.1, 2 The second-generation, TwitchView2 train-of-four (TOF) monitor makes it even easier to replicate these results.
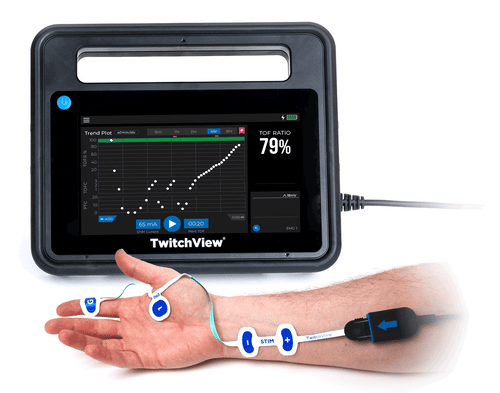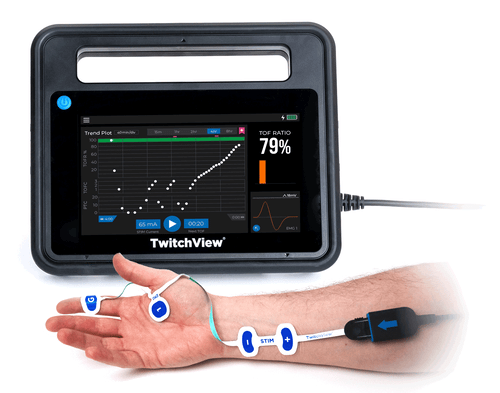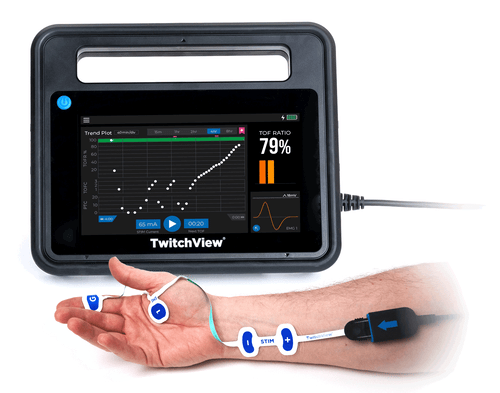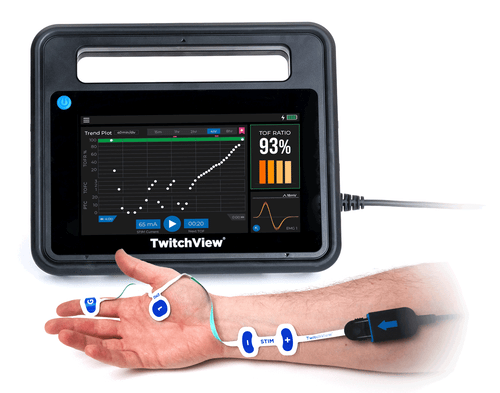
Introducing TwitchView2, a complete redesign based on experience in over 1,000,000 clinical cases around the world.
TwitchView2 is a next-generation quantitative neuromuscular monitor designed to withstand OR abuse and to perform reliably in even the most difficult-to-monitor patients. With a faster start-up, all clinically relevant data on one main display, and a workflow where the anesthetist just places the electrode and hits the START button, we’ve created the “EASY button”.
Are all EMG monitors created equal?
Electromyography (EMG) has been recommended as the new gold standard for quantitative neuromuscular monitoring [3], but every monitoring system is unique. Inherent differences in monitor software and hardware impact measurement accuracy, performance, and the ease with which a monitor can be incorporated into routine care.
At Blink, we focus on validated performance, reliability, and ease-of-use. We encourage all prospective customers to compare TwitchView head-to-head with any other monitor on the market to see the differences in performance and the impact on clinical decision-making.
 Validation in Peer-Reviewed Publications
Validation in Peer-Reviewed Publications
-
Performance Validation: TwitchView EMG is validated as accurate and interchangeable with mechanomyography (MMG) in top-tier publications.4, 5
-
Clinical Validation: TwitchView use has been proven to eliminate residual paralysis and change the management of NMB drugs, enhancing patient safety and reducing unnecessary hospital expenses.1
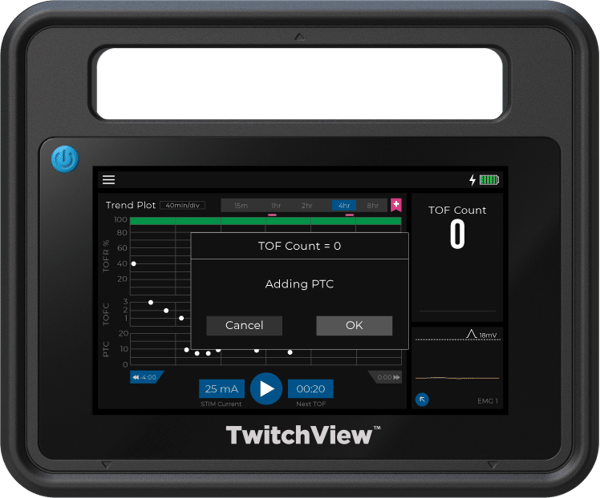
Convenient Workflow
-
User Interaction: Attach the electrode and press play to start monitoring… that’s it.
-
Automatic Monitoring: Patented AutoPTCTM mode automatically switches between TOF and PTC measurements.
-
EMR Connectivity: Eliminates manual charting in Epic, Cerner, Innovian & more. We support an open interface commitment meaning we will connect to any EMR.
Dependable Hardware
-
System Construction: Ruggedized monitor case and cable with a hospital-grade power cord.
-
Universal Mount: Proprietary mounting arm with flexible configurations to support any OR setup.
-
Made in USA: TwitchView2 was designed and built in Seattle, WA
 Advanced Algorithm
Advanced Algorithm
-
EMG Measurement Technique: Performs a comprehensive waveform analysis over thousands of data points, integrating the area under the curve (AUC) of the compound action potential alongside detection of multiple EMG signal features, to precisely identify even the smallest muscle twitches.
-
Noise Cancellation: Isolates the patient signal, capturing waveforms as small as 0.2 mV enabling reliable performance during deep block and in difficult-to-monitor patients like neonates.
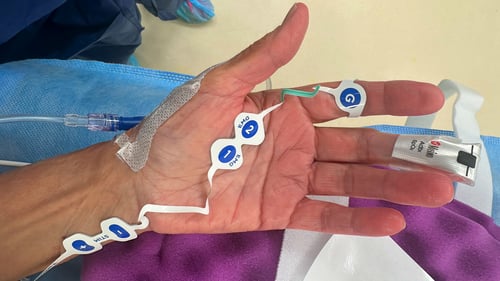
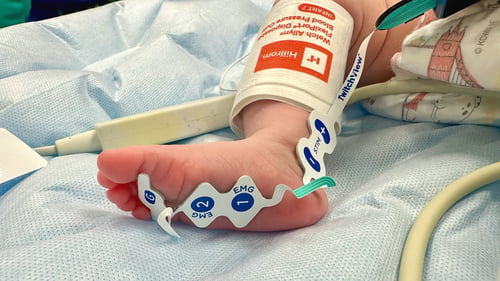
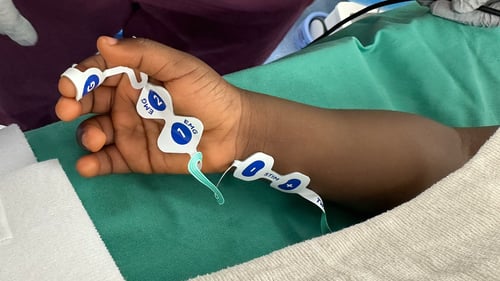
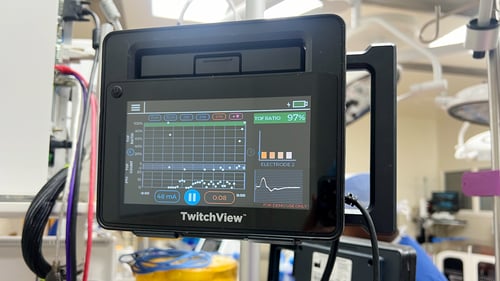
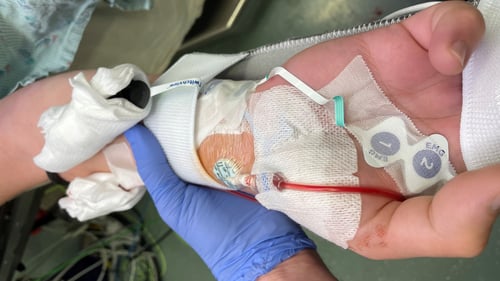
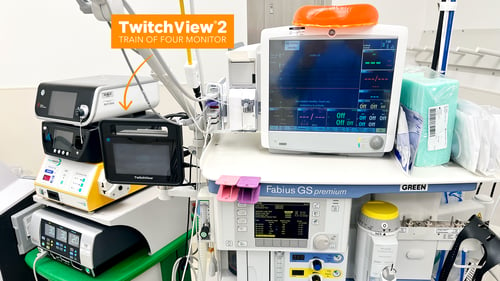
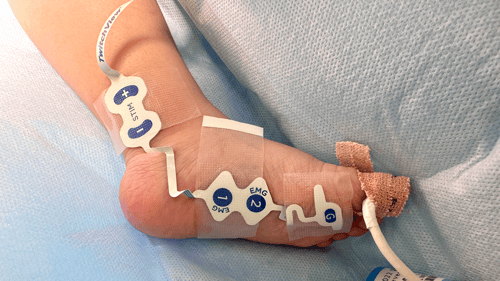
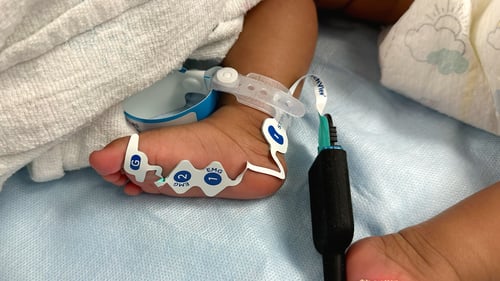
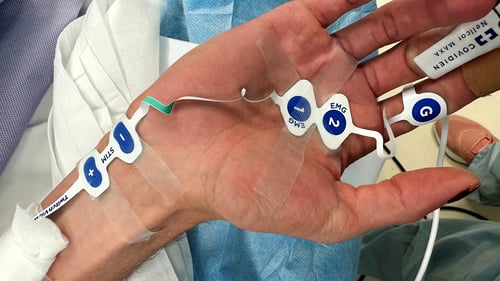
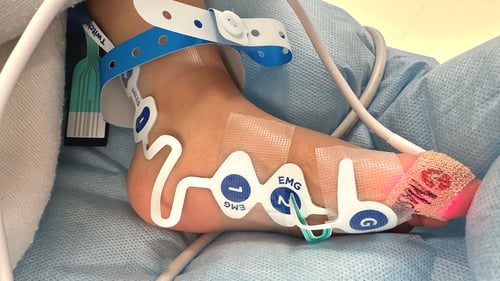
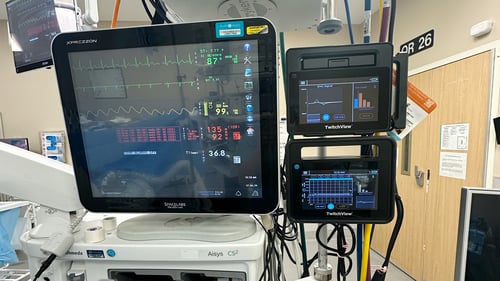
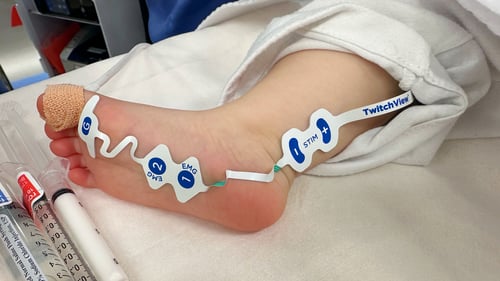
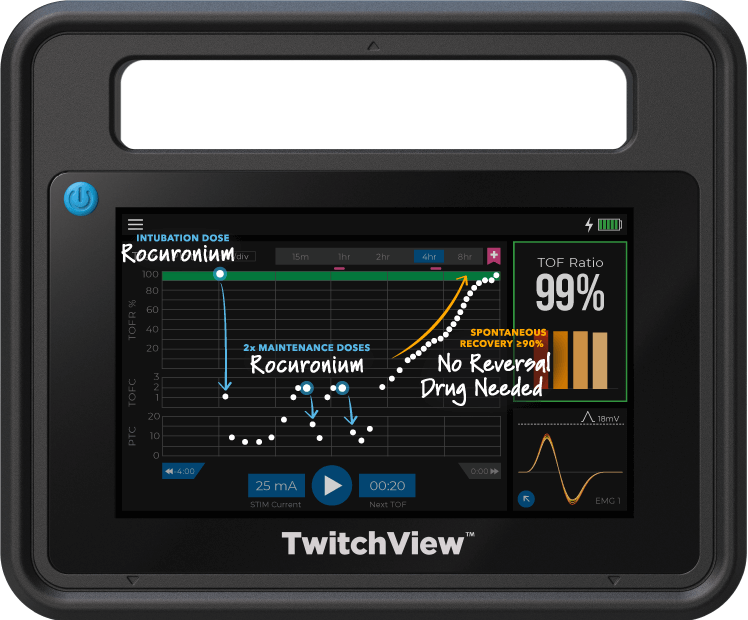
TwitchView provides continuous updates on the patient’s level of block with the Auto-PTCTM function automatically switching between TOF and PTC monitoring modes. In addition to real-time data, every measurement is plotted on the interactive trend plot, enabling clinicians to visualize how neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBA) affect each patient differently. Access to dynamic data enables anesthesia providers to dose drugs according to the individual patient and case needs—often resulting in less NMBA being administered. As demonstrated by Bowdle et al., TwitchView can be used to confirm the efficacy of smaller reversal doses and spontaneous patient recovery without pharmacologic reversal [2].
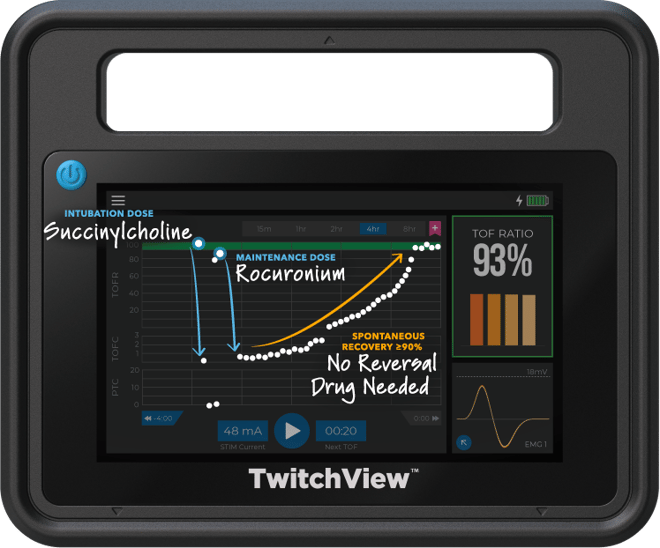
Case Type: Gastrectomy
Case Duration: 4 hours
Patient Age: 35 years
Patient Weight: 148kg
---
Electrode Size: Large
Intubation Dose: 100mg Succinylcholine
Maintenance Dose: 30mg Rocuronium
Reversal: Spontaneous Recovery
TwitchView confirms complete spontaneous recovery to a TOF Ratio ≥90%—no pharmacological reversal needed!

Case Type: Cholecystectomy
Case Duration: 2 hours
Patient Age: 87 years
Patient Weight: 87kg
---
Electrode Size: Large
Intubation Dose: 50mg Rocuronium
Maintenance Dose: 10mg Rocuronium
Reversal Dose: 200mg Sugammadex
After sugammadex administration, it took six minutes to start taking effect and 10 minutes to achieve adequate recovery (TOFR ≥90%). Two minutes after sugammadex was administered, the provider noted four twitches on the face, whereas TwitchView measured a TOF Count (TOFC) 1.
TwitchView accurately informed the provider, preventing this at-risk elderly patient from being extubated at a TOFC 1.

Case Type: Cardiac Catheterization
Case Duration: 2 hours
Patient Age: 12 years
Patient Weight: 34kg
---
Electrode Size: Medium
Intubation Dose: 34mg Rocuronium
Maintenance Doses: 2x 10mg Rocuronium
Reversal: Spontaneous Recovery
Continuous data and the trend plot inform providers of the rapid clearance of rocuronium guiding more frequent dosing. When the case is complete, TwitchView confirms spontaneous recovery was achieved, and no reversal was administered.

Case Type: Congenital Heart Defect Correction
Case Duration: 7 hours
Patient Age: 5 years
Patient Weight: 16.6kg
---
Electrode Size: Medium
Intubation Dose: 2mg/kg Rocuronium (Roc)
1st Maintenance Doses: 4x 0.6mg/kg Roc
2nd Maintenance Dose: 1mg/kg Roc
Reversal Doses: 2x 4mg/kg Sugammadex
Before bypass, TwitchView guided 0.6 mg/kg redoses every 40 minutes to maintain necessary surgical conditions. After 4 mg/kg sugammadex was administered at a PTC of 5, TwitchView indicated recovery had stalled and a second reversal dose was administered.

Case Type: Cleft Palate Repair
Case Duration: 4 hours
Patient Age: 7 months
Patient Weight: 6.7kg
---
Electrode Size: Small
Intubation Dose: 1mg/kg Rocuronium (Roc)
Maintenance Dose: None
Reversal: Spontaneous Recovery
TwitchView indicated that the induction dose of rocuronium provided sufficient surgical conditions in a 4.5-hour case and confirmed spontaneous recovery—no reversal administered.

Case Type: Pyeloplasty
Case Duration: 2 hours
Patient Age: 2 months
Patient Weight: 6kg
---
Electrode Size: Small
Intubation Dose: 1.2mg/kg Rocuronium (Roc)
Maintenance Dose: None
1st Reversal Dose: 4mg/kg
2nd Reversal Dose: 2mg/kg in PACU
4mg/kg reversal dose of sugammadex stalled at a TOFR 42%, but patient passed subjective assessment was extubated and brought to PACU. Recovery did not progress and baby was inconsolable. An additional 2 mg/kg sugammadex was administered in the PACU and baby recovered to TOFR 91%, calmed and accepted a bottle.

20% of patients achieved spontaneous recovery and did not require pharmacologic reversal when TwitchView was used to guide intraoperative drug dosing.1, 2
Reversal abstention is only possible with a quantitative neuromuscular monitor, like TwitchView distinguishing between minimal residual blockade (TOFR 40% to <90%) and adequate recovery (TOFR ≥ 90%). In a facility performing 10,000 general anesthetic cases with rocuronium each year, a 20% spontaneous recovery rate could equate to over $200,000.00 either spent or saved.
In a landmark study, Thilen et al. investigated the impact of a protocol using TwitchView to manage rocuronium blockade and reversal.
Commenting on study results first author Dr. Thilen remarked, “Using an EMG-based quantitative neuromuscular monitor [TwitchView] and a decision support guide, we achieved an unprecedented 0% incidence rate of residual neuromuscular blockade while using sugammadex for less than 50% of all patients. Approximately 20% of the patients in our mixed surgical population achieved adequate spontaneous recovery and did not need any pharmacological reversal [2]”.
With TwitchView guiding intraoperative management and reversal of neuromuscular blockade, residual paralysis was prevented, and reversal drug costs were 70% lower than universal utilization of sugammadex[1].
For a more in-depth review of Dr. Thilen’s study, visit: : How to Implement the ASA Practice Guidelines for Neuromuscular Blockade
In a groundbreaking study, Bowdle et al. used TwitchView to test the effectivity of titrated doses of sugammadex after cardiac surgery. Investigators hypothesized that many patients could be reversed with less than the label recommended dose of sugammadex and that some patients would require more to achieve adequate recovery.
- Twenty-six (20%) of the 126 patients enrolled spontaneously recovered to a TOFR ≥ 90%.
- Eighty-four out of 97 patients (87%) required less than the manufacturer’s recommended dose of sugammadex, and
- 13 (13%) required more than the manufacturer’s recommended dose [2].
In an accompanying editorial [6], Todd and Kopman comment:
We believe that this constitutes some of the strongest evidence to date for the value of routine quantitative neuromuscular blockade monitoring— and clearly demonstrates the fallacy of believing that sugammadex obviates the need for such monitoring.
For more details on the potential impact of TwitchView on block antagonism, read: How Quantitative Train of Four Impacts Rocuronium Reversal
The Potential Impact on Clinical Outcomes and the Total Cost of Care
Residual paralysis or inadequate recovery from neuromuscular blocking agents can lead to serious complications like upper airway obstruction, reintubation, pneumonia, and a prolonged hospital stay. The cause of these events is often misattributed, but the evidence is unequivocal.
The only strategy proven to eliminate residual paralysis is using quantitative neuromuscular monitoring to confirm patient recovery (TOF ratio ≥ 90%) prior to extubation [1]. However, quantitative neuromuscular monitors are more expensive than subjective methods of assessment. To determine if the increased cost was justified, Edwards et al. conducted a multimodal analysis to determine the potential clinical and financial impact of adopting quantitative neuromuscular monitoring at their academic institution.
Researchers determined that postoperative pulmonary complications cost Temple University Hospital roughly $7 million dollars annually. By contrast, the annual cost of implementing TwitchView was $162,000. As a result of the analysis, TwitchView was installed in every anesthetizing location across the Temple Health System.
By preventing residual neuromuscular blockade, anesthesia providers at Temple will improve patient outcomes and reduce hospital expenses.
"This is a real opportunity for our specialty." -Dr. Gordon Morewood
Chair and Professor of Anesthesiology
Temple University
Implementation
With you every step of the way
Our sole focus is advancing the quality and use of quantitative neuromuscular monitors. To enable the success of our hospital partners, we've developed an implementation pathway and multi-part training that we will tailor to your institution’s goals and needs.
Submit a request to start your customized plan and your regional representative will be in touch shortly. Contact us today!
- Thilen SR, Sherpa JR, James AM, Cain KC, Treggiari MM, Bhananker SM. Management of Muscle Relaxation With Rocuronium and Reversal With Neostigmine or Sugammadex Guided by Quantitative Neuromuscular Monitoring. Anesth Analg. 2023 May 12
- T. Andrew Bowdle, Kishanee J. Haththotuwegama, Srdjan Jelacic, Sharon T. Nguyen, Kei Togashi, Kelly E. Michaelsen; A Dose-finding Study of Sugammadex for Reversal of Rocuronium in Cardiac Surgery Patients and Postoperative Monitoring for Recurrent Paralysis. Anesthesiology 2023; 139:6–15
- Thilen SR, Weigel WA, Todd MM, et al. 2023 American Society of Anesthesiologists Practice Guidelines for Monitoring and Antagonism of Neuromuscular Blockade: a report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Neuromuscular Blockade. Anesthesiology2023; 138: 13–41.
- Bowdle A, et al. Counting train-of-four twitch response: comparison of palpation to mechanomyography, acceleromyography, and electromyography. Br J Anaesth. 2020;124(6):712-717.
- Bowdle A, et al. A comparison of a prototype electromyograph vs. a mechanomyograph and an acceleromygraph for assessment of neuromuscular blockade. Anesthesia. 2020;75(2): 187-195.
- Todd MM, Kopman AF. Sugammadex Is Not a Silver Bullet: Caveats Regarding Unmonitored Reversal. Anesthesiology. 2023 Jul 1;139(1):1-3.
- Edwards LA, Ly N, Shinefeld J, Morewood G. Universal quantitative neuromuscular blockade monitoring at an academic medical center - a multimodal analysis of the potential impact on clinical outcomes and total cost of care. Perioperative Care and Operating Room Management2021; 24: 100184.
The TwitchView System provides quantitative monitoring of neuromuscular transmission, allowing clinicians to evaluate the degree of neuromuscular blockade following the administration of neuromuscular blocking agents. The content on this website and blog is for reference and educational purposes only and does not replace clinical judgment. Healthcare professionals should rely on their expertise, training, and relevant guidelines to inform their decisions.




